Group Policy Object (GPO) template
Serial Port for Remote Desktop Server includes *.admx and *.adml administrative template files. These template files allow to configure the product via Local GPO and/or Domain-Based GPO. Please refer to Microsoft MSDN article on managing ADMX files.
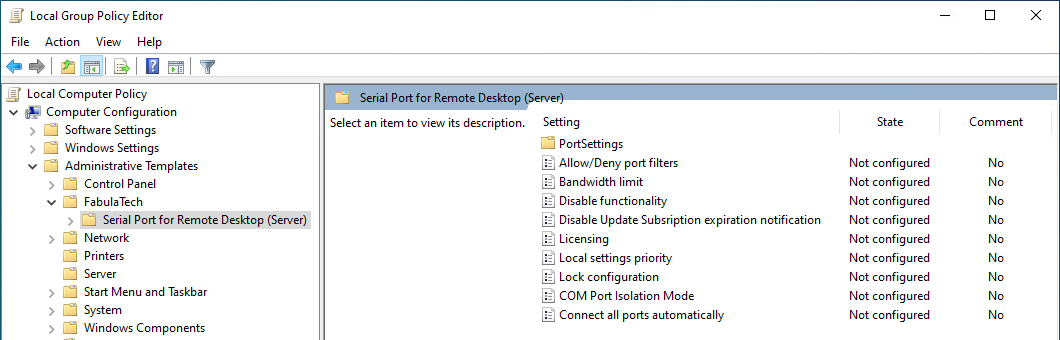
The archive file containing administrative template can be found in the installation directory:
%ProgramFiles%\FabulaTech\Serial Port for Remote Desktop (Server)\policies.zip
Additionally, the administrative template files are deployed to a local GPO during product installation and can be found here:
%WINDIR%\PolicyDefinitions\Fabulatech.admx %WINDIR%\PolicyDefinitions\ftsprrdp.admx %WINDIR%\PolicyDefinitions\en-US\Fabulatech.adml %WINDIR%\PolicyDefinitions\en-US\ftsprrdp.adml
it's recommended to use the GPO template files provided with the latest version of Serial Port for Remote Desktop Server.
The GPO template can be used to configure the following settings:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Local settings priority |
If this policy setting is enabled, the local program settings have priority over policy settings. If this policy setting is disabled or not configured, policy settings have priority over local program settings. Within the scope of each type of settings, the settings set for the computer always have priority over settings set for the user. If this policy setting is set for the computer, it has priority over policy setting set for the user. |
| Disable functionality |
If this policy setting is enabled, the connection with the workstation side is not established, the ports are not redirected. If this policy setting is disabled, the Serial COM works in usual mode. If this policy setting is not configured, the disabling functionality is determined by local program settings. |
| Connect all ports automatically |
If this policy setting is enabled, all client COM ports will be automatically connected (even if no individual GPO is configured). If there are individual GPO settings configured for some of the ports, the individual port GPO settings are used. If this policy setting is disabled or not configured, the auto-connect functionality is determined by individual port GPO or local program settings. |
| COM Port Isolation Mode |
If Full Isolation mode is chosen, virtual serial ports are visible and accessible within user sessions only. In this mode COM port names can have the same names in different user sessions. Important: system services (like spoolsrv.exe) are not able to access isolated serial ports in such case. If Strict Isolation mode is chosen, virtual serial ports are visible and accessible within user sessions and only withing the processes run under the owner of the session. This means that the processes started using "Run as Administrator", or the processes started using PsExec utility will not be able to see and access the redirected serial ports. If Isolation Disabled mode is chosen, virtual serial ports are visible globally. Any port can be accessed from any session. Limitation: port names must be unique for every user (so the ports cannot have the same names in different user sessions). Important: system services (like spoolsrv.exe) can access any serial ports. If this policy setting is not configured, Serial Redirection operates in the default mode:
|
| Lock configuration |
If this policy setting is enabled, the user interface containing the program settings is locked and the user can't change settings in the tray menu. If this policy setting is disabled, the user interface containing the program settings is accessible for users. If this policy setting is not configured, the blocking of the configuration is determined by local program settings. If this policy setting is configured for the computer, it has priority over policy setting configured for the user. |
| Bandwidth limit |
If this policy setting is enabled, the data transfer speed between the server and all workstations is limited by the specified kilobytes per second.The value "0" disables speed limitation If this policy setting is disabled, the speed limitation is disabled. If this policy setting is not configured, the speed limitation is determined by local program settings. |
| Allow/Deny port filters |
If this policy is enabled, the Allow and Deny filers are used in order to decide if every specific COM port detected on the Workstation side is allowed for redirection or not. In case if some port is not allowed for redirection, the Server side will threat it as if the port does not even exist on the Workstation side. The lists use USB device properties of the COM port's rules. Example: USB:067B:2303:* USBPATH:1-4 WINDEVID:*ACPI* PORTNAME:COM3 PORTNAME:COM5 Syntax:
Examples: USB:067B:2303:400 – matches the USB device with the specified VID, PID and Revision. USB\VID_067B&PID_2303&REV_0400 USB:067B:2303:* – matches any USB device with the specified VID and PID and any Revision. USB\VID_067B&PID_2303 USB:067B:* – matches any USB device with the specified VID and any PID and any Revision. USB\VID_067B USB:* – matches any USB device USBPATH:1-2-1 – matches the identificator of the USB port where the device is plugged physically WINDEVID:* – matches any HardwareID string WINDEVID:*ACPI* – matches a HardwareID string containing ACPI substring PORTNAME:COM3 – matches only "COM3" serial port PORTNAME:*M3 – matches serial ports with the names ending with "M3". E.g. COM3, VCOM3. PORTNAME:*M3* – matches serial ports with names containing "M3" substring. E.g. COM3, COM33, VCOM333. PORTNAME:/dev/ttys* – matches all "/dev/ttys" devices. E.g. /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyS5.
Remarks: |
| PortSettings |
This policy setting is used for configuring certain port parameters that are used for their redirection:
If this policy setting is enabled, its parameters are used during port redirection. If this policy setting is disabled or not configured, parameters specified in local program settings are used for port redirection. If this policy setting is configured for the computer, it has priority over policy setting configured for the user. |
| Disable Update Subscription Expiration Notification |
This policy setting controls whether update subscription expiration notifications are displayed.
If Enabled, the update subscription expiration notifications will not appear. This policy setting overrides any user-configured preferences, meaning users cannot change the update subscription notification mode through the user interface. |
| Licensing |
This policy setting is used for licensing management. The following licensing modes are used:
For "License Key" type of licensing you must specify a string of the key in the corresponding field. For "License Server" type of licensing you must specify a license server name in the name_or_ip:port format, where the port is an optional parameter. If this policy setting is enabled, the licensing mode will be overridden by this policy setting. It means using GPO License key instead key that determined via the settings interface. If this policy setting is disabled or not configured, the licensing mode is determined via the settings interface. |